Mind Tricks: Understanding the Science Behind Optical Illusions

Read time: 5 minutes
The human brain is an extraordinary processing machine, constantly interpreting and reconstructing the visual information it receives. Optical illusions reveal the remarkable and sometimes mysterious ways our brain makes sense of the world, exposing the complex mechanisms behind human perception.
The Brain's Visual Interpretation Workshop
Our eyes are not cameras that simply record reality. Instead, they are intricate sensors that capture light, which the brain then interprets, predicts, and sometimes dramatically reimagines. Optical illusions demonstrate how this interpretation can be manipulated, revealing the brain's predictive and creative nature.
Historical Context of Visual Deception
Humans have been fascinated by visual trickery for thousands of years. Ancient Greek and Egyptian artists deliberately used geometric patterns and perspective techniques to create visual effects that challenged viewers' perceptions. Renaissance painters like Leonardo da Vinci experimented with techniques that could make two-dimensional surfaces appear three-dimensional, laying groundwork for understanding how our brains process visual information.
Types of Optical Illusions
Scientific researchers categorize optical illusions into several fascinating types. Physiological illusions emerge from excessive stimulation of specific types of receptors in our eyes or brain. Cognitive illusions leverage the brain's tendency to make assumptions and fill in missing information based on past experiences and expectations. Some illusions play with color perception, making stationary images appear to move or transform. Others manipulate depth perception, creating impossible geometric shapes or making flat surfaces seem three-dimensional. These illusions aren't mistakes—they're windows into how our visual system processes and interprets information.
Famous Optical Illusions
To truly appreciate the science behind optical illusions, let’s explore a few famous examples that have captivated and puzzled minds for generations. These illusions highlight the brain’s remarkable interpretation mechanisms and underscore why our perception of reality can be so easily manipulated.
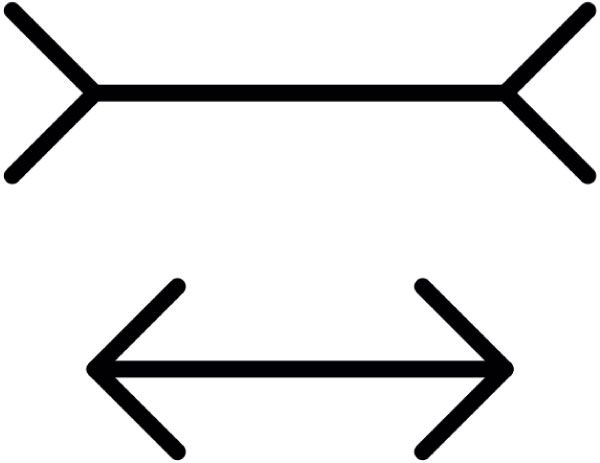
The Müller-Lyer Illusion
This classic illusion features two lines of identical length that appear unequal due to their arrow-like endings: one line has inward-facing arrows, making it seem shorter, while the other has outward-facing arrows, making it seem longer. The brain interprets these lines based on learned assumptions about depth and perspective, with the outward-facing arrows mimicking the edges of distant objects, leading to the perception of greater length. This phenomenon highlights how contextual cues can override the actual physical dimensions of an image.
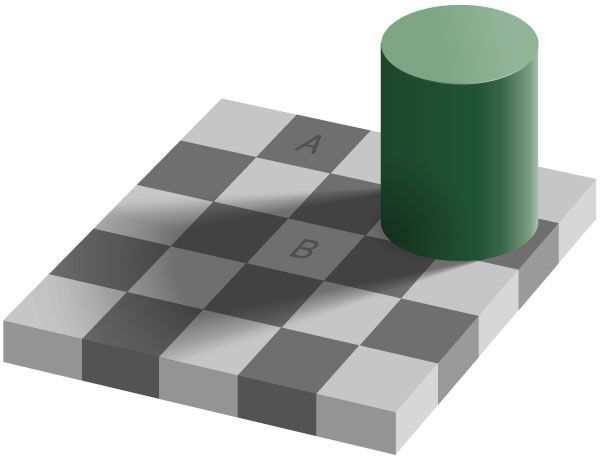
The Checker Shadow Illusion
Created by Edward Adelson, this illusion features a checkerboard pattern with a shadow cast over part of it, where a dark square in the shadow and a light square outside the shadow appear to be different shades despite being the same color. The brain interprets the colors by factoring in the shadow and adjusting its perception based on expected lighting conditions, assuming the shaded square should be darker and the lighter square brighter, demonstrating the brain’s reliance on environmental context to process color and brightness.
Note: In the example, square A and B are the exact same color.
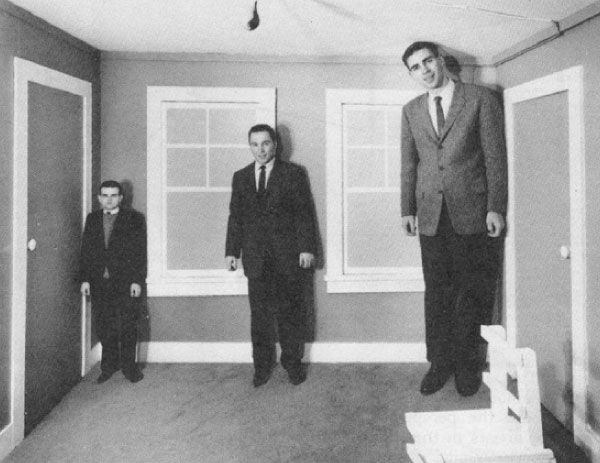

The Ames Room
The Ames Room is a distorted room that creates a striking visual effect where people standing in different corners appear drastically different in size, with one looking like a giant and another appearing tiny. This illusion occurs because the room’s construction features slanted walls and a tilted floor, but it is viewed through a peephole that limits depth perception. The brain assumes the room is a standard rectangular shape, distorting the perceived size of the people based on their positions, revealing how the brain applies assumptions about geometry and scale.

The Spinning Dancer
The Spinning Dancer is an optical illusion featuring a silhouetted figure that some viewers perceive as spinning clockwise, while others see her spinning counterclockwise. This ambiguous illusion occurs because the brain lacks sufficient depth cues to determine the figure’s orientation, causing perception to flip between two plausible interpretations. It highlights how the brain resolves ambiguity by toggling between equally valid scenarios.
Neurological Mechanisms at Play
Modern neuroscience has uncovered fascinating insights into why optical illusions work. Different parts of the brain process various visual elements—color, movement, depth, and shape—in parallel. When these systems receive conflicting information, the brain attempts to resolve the discrepancy, often resulting in the perceptual "tricks" we experience as illusions. The illusions detailed above, from the Müller-Lyer illusion’s reliance on contextual cues to the Ames Room’s spatial manipulation, illustrate the intricate interplay of visual systems.
Practical and Scientific Significance
Optical illusions are more than just entertaining curiosities. They provide critical insights into human cognitive processing, helping researchers understand brain function, visual perception, and neurological conditions. Studying how and why our brains are "fooled" helps develop treatments for visual disorders and advances our understanding of neural plasticity.
Cultural and Artistic Expressions
Artists and designers have long exploited optical illusion principles. From MC Escher's impossible geometric landscapes to modern digital art, creators use our brain's perceptual quirks to challenge viewers' understanding of reality. Street artists create massive, hyper-realistic 3D drawings that seemingly transform urban landscapes.
Technological Applications
The science of optical illusions has practical applications in fields ranging from virtual reality to camouflage design. Military researchers study these principles to develop advanced concealment techniques, while technology companies use optical illusion principles in user interface design to guide attention and improve user experience.
The Takeaway
Optical illusions remind us that reality is not a fixed, objective experience but a dynamic, constructed interpretation. They reveal the brain's incredible ability to predict, adapt, and creatively process information, transforming simple visual inputs into complex, meaningful experiences.
Far from being mere tricks, these illusions are profound demonstrations of human cognitive complexity—a reminder that how we see the world is as much about what happens in our minds as what enters our eyes.
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. It is strongly recommended to consult with an eye care professional for personalized recommendations and guidance regarding your individual needs and eye health concerns.
All of Urban Optiks Optometry's blog posts and articles contain information carefully curated from openly sourced materials available in the public domain. We strive to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information provided. For a comprehensive understanding of our practices and to read our full disclosure statement, please click here.
OUR LATEST POSTS
© Urban Optiks Optometry, Inc. 2009-2025
All Rights Reserved
Location
The Cairo Building
3788 Park Blvd, Suite 5
San Diego, CA 92103
Phone: 619.683.2020
Text: 619.683.2020
Fax: 619.683.2111
Email: info@uoosd.com
Hours
Monday: 9 am – 7 pm
Tuesday: 9 am – 6 pm
Wednesday: 9 am – 6 pm
Thursday: 9 am – 7 pm
Friday: 9 am – 6 pm
Saturday: 9 am – 5 pm
Sunday: Closed