Virtual Reality and Its Effects on Eye Strain

Read time: 4 minutes
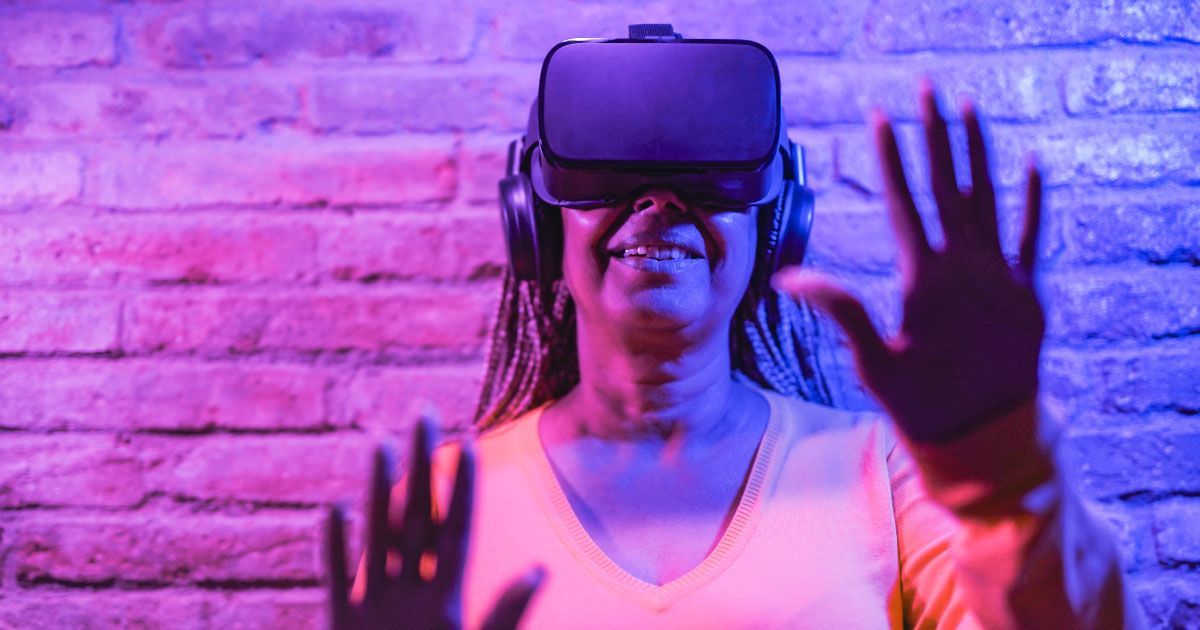
Virtual reality (VR) technology has revolutionized the way people experience gaming, education, and even workplace training. By immersing users in fully digital environments, VR creates a sense of presence and interaction unlike anything achievable with traditional screens. However, as VR devices become more common, concerns about their impact on eye health - particularly eye strain - have grown. Understanding how VR affects vision and what can be done to reduce potential strain is essential for users to enjoy the technology safely.
How VR Works and Its Impact on the Eyes
VR headsets work by placing small, high-resolution screens close to the eyes and using lenses to project images in a way that mimics depth and distance. These devices create a stereoscopic effect, tricking the brain into perceiving a 3D environment. While this immersive experience is impressive, the mechanics of VR place significant demands on the visual system.
One key issue is the "vergence-accommodation conflict." In real-world settings, the eyes adjust focus (accommodation) and angle (vergence) simultaneously to look at objects at different distances. VR disrupts this natural process because the eyes focus on a fixed screen just centimeters away, even as they converge to "look at" objects that appear to be at varying distances. This mismatch can strain the eye muscles, leading to discomfort over time.
Symptoms of VR-Related Eye Strain
Eye strain, or asthenopia, occurs when the eyes are overworked or stressed. Common symptoms experienced during or after VR use include:
- Dryness or irritation in the eyes
- Blurry or double vision
- Headaches
- Difficulty refocusing on real-world objects
- Fatigue or a general sense of discomfort around the eyes
These symptoms can vary depending on factors like the duration of VR use, the quality of the headset, and the user’s individual eye health.
Factors That Contribute to Eye Strain
Several factors influence the likelihood and severity of VR-related eye strain:
- Prolonged Use: Spending extended periods in VR without breaks can intensify strain. Unlike watching TV or using a computer, VR fully engages the visual system without allowing for natural pauses, such as looking around a room or out a window.
- Screen Quality: The resolution, refresh rate, and field of view of a VR headset can impact eye strain. Low-resolution screens may cause pixelation, while a low refresh rate can lead to motion blur, both of which stress the eyes.
- Interpupillary Distance (IPD): This refers to the distance between the centers of the user’s pupils. Many VR headsets allow users to adjust the IPD to match their eyes, but improper settings can lead to misalignment and discomfort. Learn more about Pupillary Distance in our blog post "Unlocking the Mystery of PD"
- Lighting and Contrast: High contrast and artificial lighting in VR environments can exacerbate strain, especially when transitioning back to natural light.
Reducing the Risk of Eye Strain
Fortunately, there are ways to minimize the impact of VR on the eyes. The most effective strategies include:
- Taking Breaks: Experts recommend following the "20-20-20 rule": every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and focus on something 20 feet away. This helps relax the eye muscles and reduce fatigue.
- Adjusting Settings: Properly configuring the headset’s IPD and ensuring a clear focus can prevent unnecessary strain. Many modern devices include guides or automatic adjustments to assist with this.
- Limiting Sessions: Reducing the amount of time spent in VR can prevent symptoms from escalating. For example, starting with shorter sessions and gradually increasing duration may help the eyes adapt.
- Using Quality Equipment: Investing in a high-resolution headset with a fast refresh rate can improve comfort. Devices with adjustable lenses and ergonomic designs are particularly beneficial.
- Practicing Eye Exercises: Simple exercises, like shifting focus between near and distant objects, can help maintain eye flexibility and reduce strain.
Long-Term Considerations
While current research on VR and long-term eye health is limited, most experts agree that moderate use is unlikely to cause permanent damage. However, users with preexisting conditions, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, or binocular vision disorders, may be more susceptible to discomfort. Children, whose visual systems are still developing, may also be at higher risk and should use VR cautiously and under supervision.
Future advancements in VR technology may further mitigate the risks of eye strain. For instance, developers are exploring adaptive focus displays that better mimic natural vision and reduce the vergence-accommodation conflict. As these innovations become mainstream, the visual experience of VR is likely to become more comfortable and accessible.
The Takeaway
Virtual reality offers incredible opportunities for entertainment, education, and innovation, but it also comes with challenges for eye health. Understanding the causes of VR-related eye strain and taking proactive steps to minimize its effects can help users enjoy the technology without discomfort. By balancing immersive experiences with mindful usage, VR enthusiasts can protect their vision while exploring new virtual worlds.
Do you have concerns about the effects of virtual reality and digital devices on your eyes? Be sure to discuss them with your eye doctor at your next eye exam. Comprehensive eye exams are more than just a prescription for glasses - they assess the overall health of your eyes and can detect early signs of over 100 diseases and eye conditions. Schedule your eye exam today!
Share this blog post on social or with a friend:
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. It is strongly recommended to consult with an eye care professional for personalized recommendations and guidance regarding your individual needs and eye health concerns.
All of Urban Optiks Optometry's blog posts and articles contain information carefully curated from openly sourced materials available in the public domain. We strive to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information provided. For a comprehensive understanding of our practices and to read our full disclosure statement, please click here.