Navigating the Shadows of Diabetic Retinopathy
Read time: 4 minutes
Diabetes and Vision
Diabetic retinopathy, a condition affecting the eyes, stands as a stark reminder of the intricate relationship between diabetes and vision. Let’s discover the historical and contemporary information about diabetic retinopathy, understand its causes, explore treatment options, and shed light on the importance of proactive eye care in the face of diabetes.
Historical Context: Tracing the Shadows of Diabetic Retinopathy
The roots of our understanding of diabetic retinopathy extend deep into the past. While diabetes itself has been recognized for centuries, it wasn't until the 19th and 20th centuries that the ocular complications of diabetes, including retinopathy, began to be systematically studied. Early physicians noted the link between diabetes and vision problems, laying the foundation for contemporary research and interventions.
Defining Diabetic Retinopathy
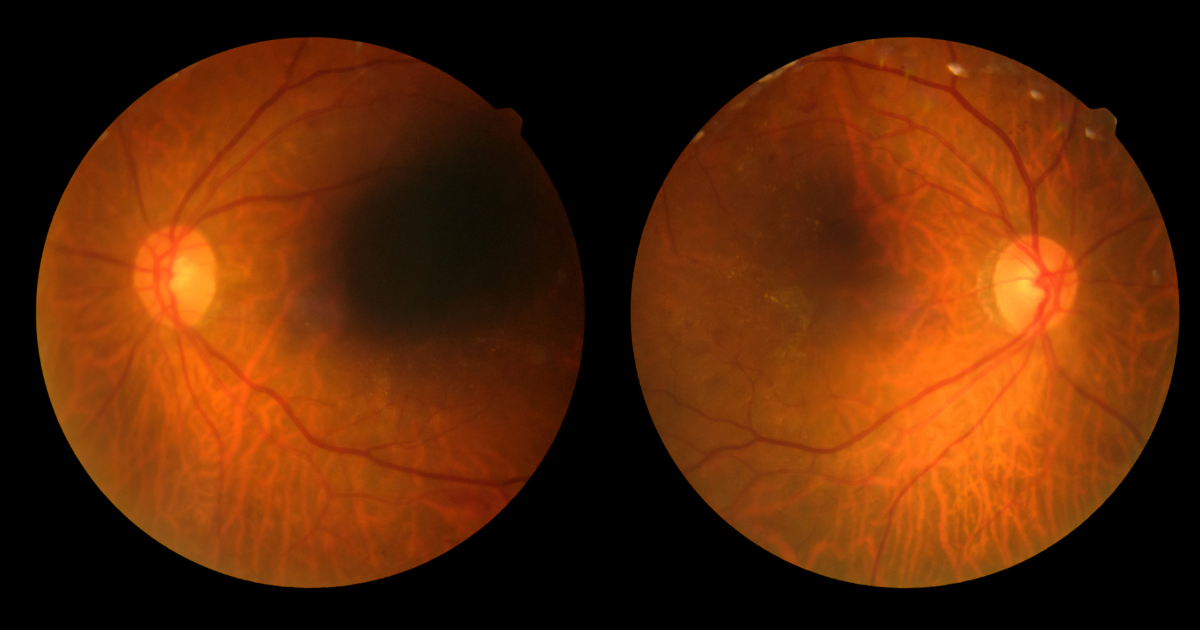
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that affects the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It is a complication of diabetes, both type 1 and type 2, resulting from high blood sugar levels damaging the blood vessels in the retina. The condition often develops gradually, initially showing mild symptoms that can progress to severe vision impairment if left untreated.
Understanding the Causes: The Interplay Between Blood Sugar and Blood Vessels
The primary cause of diabetic retinopathy lies in the prolonged exposure of the retina's blood vessels to elevated levels of blood sugar. The intricate network of vessels that nourish the retina becomes compromised, leading to a cascade of events:
- Early Stage (Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy): In this stage, the blood vessels weaken and develop tiny bulges. These microaneurysms can leak fluid into the retina, causing mild vision changes.
- Advanced Stage (Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy): As the condition progresses, the body attempts to compensate for the damaged vessels by growing new ones. However, these new vessels are fragile and prone to bleeding, leading to more severe vision problems, including blindness if left untreated.
Contemporary Insights
Diabetic retinopathy remains a significant public health concern. The prevalence of diabetes worldwide, coupled with the persistent challenges of managing blood sugar levels, underscores the urgency of addressing this condition. Advanced diagnostic tools, such as retinal imaging and optical coherence tomography (OCT), empower healthcare professionals to detect and monitor diabetic retinopathy with greater precision.
Risk Factors: Beyond Blood Sugar Control
While elevated blood sugar levels are the primary cause of diabetic retinopathy, other factors can heighten the risk and severity of the condition. These include:
- Duration of Diabetes: The longer an individual has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Blood Pressure Levels: Hypertension can exacerbate the damage to retinal blood vessels.
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes or diabetic retinopathy may increase susceptibility.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans and Hispanics, are at a higher risk.
Symptoms: Navigating the Shadows of Vision Changes
Diabetic retinopathy often progresses without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition advances, individuals may experience:
- Blurred or Distorted Vision: Fluid leakage and swelling in the retina can lead to changes in vision clarity.
- Floaters: The presence of dark spots or floaters may indicate bleeding into the vitreous, the gel-like substance inside the eye.
- Impaired Color Vision: Colors may appear less vibrant or distorted.
Treatment Options: Illuminating the Path to Vision Preservation
Effective management of diabetic retinopathy involves a multifaceted approach, emphasizing blood sugar control, regular eye screenings, and, when necessary, targeted interventions. Here are key components of a treatment plan:
- Blood Sugar Management: Strict control of blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle modifications is fundamental to preventing and slowing the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
- Blood Pressure Control: Managing hypertension is crucial, as it helps mitigate the risk of complications and slows the progression of the condition.
- Laser Therapy: In cases of advanced diabetic retinopathy, laser therapy (photocoagulation) may be employed to seal leaking blood vessels and reduce the growth of abnormal vessels.
- Anti-VEGF Injections: Intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) medications can help reduce swelling and prevent the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
- Vitrectomy: In severe cases where bleeding into the vitreous is significant, a surgical procedure called vitrectomy may be necessary to remove blood and scar tissue.
The Role of Routine Eye Exams: A Proactive Approach
Regular eye examinations are pivotal in the early detection and management of diabetic retinopathy. Even in the absence of symptoms, these exams allow healthcare professionals to identify changes in the retina and initiate interventions to preserve vision. The American Diabetes Association recommends annual comprehensive eye exams for individuals with diabetes.
Future Horizons: Research and Innovations
Ongoing diabetic retinopathy research holds promise for future advancements. From exploring new pharmacological interventions to investigating the potential of artificial intelligence in early detection, the scientific community remains committed to enhancing our understanding and management of this complex condition.
Illuminating the Path Ahead
Within the complex landscape of diabetic retinopathy, the threads of history, current challenges, and future prospects come together. As individuals with diabetes grasp the reasons, identify symptoms, and adopt proactive management approaches, they can skillfully navigate the challenges to their vision. Routine comprehensive eye exams, diligent blood sugar management, and advancements in treatment options all work together to brighten the path toward preserving eyesight.
Share this blog post on social or with a friend:
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. It is strongly recommended to consult with an eye care professional for personalized recommendations and guidance regarding your individual needs and eye health concerns.
All of Urban Optiks Optometry's blog posts and articles contain information carefully curated from openly sourced materials available in the public domain. We strive to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information provided. For a comprehensive understanding of our practices and to read our full disclosure statement, please click here.